AWS VPC Route Server: The Game-Changer for Dynamic Routing You've Been Waiting For
- Stephen Jones
- Dev ops
- September 6, 2025
Table of Contents
Summary
AWS just dropped a networking feature that’s going to change how we think about VPC routing forever. VPC Route Server brings dynamic routing capabilities directly into your VPC, automatically handling failover scenarios that used to require complex scripting or third-party solutions. If you’ve ever wrestled with static routes and manual failover for network appliances, this one’s for you.
Objectives
By the end of this deep dive, you’ll understand:
- What VPC Route Server actually does (and why it matters)
- How it handles automatic failover using BGP and BFD
- Real-world scenarios where this solves major pain points
- Step-by-step implementation approach
The Problem VPC Route Server Solves
Picture this: You’ve got a pair of firewall appliances running on EC2 instances in your VPC. One’s active, one’s standby. When the active firewall dies, you need traffic to automatically route to the standby.
Before VPC Route Server, your options were:
- Static routes with manual intervention (not exactly “highly available”)
- Lambda functions monitoring health checks (works, but adds complexity)
- Third-party routing solutions (more moving parts, more cost)
VPC Route Server eliminates this headache by bringing enterprise-grade dynamic routing directly into AWS networking.
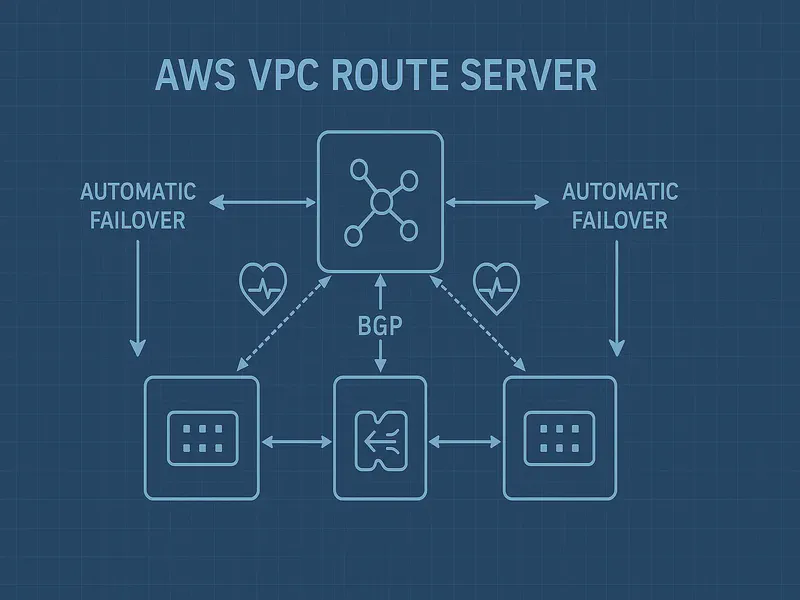
How VPC Route Server Actually Works
VPC Route Server is essentially AWS-managed BGP infrastructure that lives inside your VPC. Here’s the magic:
The Core Components
Route Server: The brain that maintains your Routing Information Base (RIB) and Forwarding Information Base (FIB). Think of it as your centralized routing decision engine.
Route Server Endpoints: AWS-managed components deployed in your subnets that handle BGP sessions with your network devices.
Route Server Peers: BGP sessions between the endpoints and your actual network appliances (firewalls, load balancers, etc.).
The Failover Flow
- Your network devices establish BGP sessions with route server endpoints
- Each device advertises routes with BGP attributes (like MED for preference)
- Route server installs the best routes in your VPC route tables
- When a device fails, BFD (Bidirectional Forwarding Detection) detects it instantly
- Route server automatically withdraws failed routes and promotes backup paths
- Traffic seamlessly flows to healthy devices
Real-World Use Cases
Scenario 1: Dual Firewall Setup
You’ve got two firewall appliances in different AZs. Device A advertises routes with MED=0 (preferred), Device B with MED=100 (backup). When Device A fails, traffic automatically shifts to Device B without any manual intervention.
Scenario 2: Multi-Vendor Network Functions
Running different network security functions from various vendors? VPC Route Server doesn’t care about the underlying technology—as long as it speaks BGP, it works.
Scenario 3: Hybrid Cloud Connectivity
Need dynamic routing between your VPC workloads and on-premises networks through network appliances? Route Server handles the complexity while you focus on business logic.
Implementation Walkthrough
Here’s the high-level setup process:
Step 1: iam Permissions
# Your EC2 instances need permissions to interact with route server
aws iam create-role --role-name VPCRouteServerRole --assume-role-policy-document file://trust-policy.json
Step 2: Create the Route Server
aws ec2 create-route-server --name MyRouteServer
Step 3: Associate with Your VPC
aws ec2 create-route-server-association \
--route-server-id rs-1234567890abcdef0 \
--vpc-id vpc-12345678
Step 4: Deploy Route Server Endpoints
aws ec2 create-route-server-endpoint \
--route-server-id rs-1234567890abcdef0 \
--subnet-id subnet-12345678
Step 5: Enable Route Propagation
aws ec2 enable-route-server-propagation \
--route-table-id rtb-12345678 \
--route-server-id rs-1234567890abcdef0
Step 6: Configure BGP on Your Devices
Your network appliances initiate BGP sessions to the route server endpoints. The exact configuration depends on your device, but the concept is universal.
What Makes This Different
Native AWS Integration: No third-party software or complex Lambda functions. This is built into the VPC fabric.
Automatic Failover: BFD detection means sub-second failover times, not the minutes you might see with health check polling.
Route Table Integration: Routes are installed directly in VPC route tables—no overlay networks or tunneling complexity.
Multi-Protocol Support: Handles both IPv4 and IPv6 routing seamlessly.
Limitations to Know About
- No VGW Support: Virtual private gateway route tables aren’t supported (use Transit Gateway Connect for that)
- BGP Requirement: Your devices must support BGP—no getting around this
- Subnet Placement: Route server endpoints consume IP addresses in your subnets
Cost Considerations
VPC Route Server follows AWS’s typical pricing model—you pay for what you use. Check the VPC pricing page for current rates, but expect charges for:
- Route server instances
- Route server endpoints
- Data processing
For most enterprise use cases, the operational savings from automated failover far outweigh the service costs.
When Should You Use This?
Perfect for:
- High-availability network appliance deployments
- Multi-vendor network function environments
- Scenarios requiring sub-second failover
- Complex routing topologies with multiple paths
Skip it if:
- You’re running simple, single-appliance setups
- Your devices don’t support BGP
- You’re happy with existing Lambda-based failover solutions
Deliverables
VPC Route Server represents a significant step forward in AWS networking capabilities. It brings enterprise-grade dynamic routing directly into the VPC fabric, eliminating the operational overhead of managing failover scenarios manually.
Key takeaways:
- Automatic failover through BGP and BFD integration
- Native VPC integration without overlay complexity
- Multi-protocol support for IPv4 and IPv6
- Enterprise-ready with sub-second failover capabilities
If you’re running network appliances in AWS and dealing with failover complexity, VPC Route Server deserves a spot on your evaluation list. The operational simplicity alone makes it worth considering for your next high-availability deployment.
Want to dive deeper into AWS networking? Follow me for more cloud architecture insights and real-world AWS implementations. What’s your biggest VPC routing challenge? Drop it in the comments below.